|
THE GRAND JUNCTION CANAL
A HIGHWAY
LAID WITH
WATER.
THE ROUTE:
III. ― UXBRIDGE TO
BRENTFORD,
AND THE
PADDINGTON ARM
“UXBRIDGE, a market town in
Middlesex, 15 miles W. from London, in the road to Oxford, is
situated on the river Coln and Grand Junction Canal, over each of
which it has a bridge . . . . This town, which is governed by two
bailiffs, two constables, and four headboroughs, is principally
noted for its very great corn market, and for its opulent mealmen,
who are chiefly Quakers, and are supposed to influence the price of
corn in the London market: on the river are many powerful flour
mills, and a vast deal of malt is made in the neighbourhood.
During the summer season, a passage-boat constantly plies to and
from London, which is highly advantageous to the inhabitants.”
A Pocket Companion for the tour of London and its
Environs (1811)
|
 |
 |
|
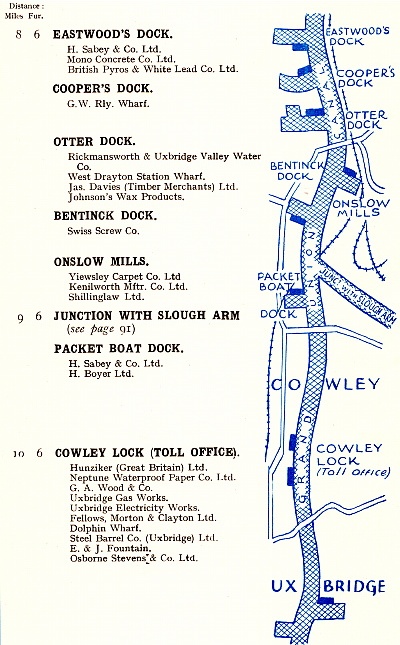
Grand Union
Canal Company route map c.1938, showing the wharves and docks that
lay between Uxbridge and Brentford. |
At Uxbridge, the Canal forms the borough’s western boundary.
Following its opening in 1794, waterborne commerce soon sprang up
accompanied by extensive wharves:
“The Grand Junction Canal, for the making of which an act of
parliament was obtained in 1793, passes by this town. It was begun
by cutting on Uxbridge Moor the first of May of that year. The
principal articles of commerce on that canal are flour, grain and
coals. . . . The following is an accurate statement of the
quantities [tons] of the different articles conveyed from the
Thames at Brentford to Uxbridge, and from Uxbridge to the Thames, in
the year 1799 (obligingly communicated by Benjamin Way, Esq). . . .”
|
Flour |
4,612 |
Lime |
14 |
|
Grain |
4,968 |
Manure |
164 |
|
Coals |
6,650 |
Coke |
68 |
|
Ashes |
1,318 |
Loam |
49 |
|
Stone |
108 |
Timber |
18 |
| Tiles & brick |
131 |
Sundries |
1,821 |
An historical account of those parishes in the
county of Middlesex,
Rev. Daniel Lysons M.A. (1800)
The writer does not distinguish between
imports and exports, but grain and coal are likely to have been
among the former, and flour the latter. Although flour milling
has now ceased, Uxbridge was once a long established flour milling
centre covering a wide area, and for some two centuries it produced
most of London’s flour. The town’s last mill, the
‘William King Flourmill’, stood on the canal bank just above Town
Lock and a large proportion of its wheat was delivered there by
narrow boats direct from Limehouse or Brentford. The mill’s
engine room, equipped with a magnificent 80hp Robey horizontal
tandem compound condensing engine, was apparently a sight to behold,
while the nearby boiler house sported two spotlessly clean
Lancashire boilers. A 50hp Gilkes water turbine supplied
stand-by power using the 7ft head across the Town Lock where there
is no shortage of water, for this stretch of the Canal is amply
supplied by the River Colne. Although William King’s Mill
ceased working in 2001, its name lives on in the popular
Kingsmill brand of bread.
Following the opening of the Paddington Arm in 1801, a passenger
service commenced between Uxbridge and the Metropolis.
Initially run by the Company, the service was later franchised to
Thomas Homer for £750 per year. The ‘packet boat’, whose crews
were noted for their smart blue uniforms with yellow capes and
yellow buttons, seems to have been well used at first, but the
journey time was too long and the service was discontinued after
several years. Homer, who had been Superintendent to the Grand
Junction Canal Company, went on to be the instigator of the Regent’s
Canal and was employed as Company Secretary, but in 1815 he was
convicted of embezzling £4,000 and sentenced to seven years’
transportation.

As well as supporting existing industry the Canal’s impact on
Uxbridge ― as with many other places ― was to open up new industrial
development. By 1814 a mill had been built for the manufacture
of plate-glass, and other industrial premises that were later set up
near the Canal included a gas-works, parchment works and mills for
processing oil, mustard and flour. Indeed, the waterway
continued to provide the town with an important trading link well
into the 20th Century:
“At Uxbridge are situated large gas and electricity undertakings,
both of which receive their supplies of coal by canal. Messrs
Fellows, Morton and Clayton Ltd. have another depot at this point
and a repair dock for their boats. There are also a number of
wharves in this locality for handling large quantities of grain and
timber.”
Grand Union Canal Company
advertising material, c.
1938
The Uxbridge Boat Centre, just to the south of Bridge 186
(Rockingham Road), was once the boatyard of Fellows, Morton and
Clayton Ltd., one of the largest carrying companies on the Canal,
which ran the yard until they ceased trading in 1948. FMC
built many of their own boats, their yard at Saltney in Birmingham
specialising in metal and wood composite construction while that at
Uxbridge built wooden boats (their last new boat, the Clent,
was built in 1947). Wooden boats were cheaper to build, the
expectation being that they would be worn out long before the rot of
old age set in.
|
 |
|
Frays, one of a
pair of new barges designed to transport
building
aggregates on the Uxbridge section of the Canal. |
Despite the general demise of canal
carrying, the Uxbridge section of the canal recently experienced a
modest return to commercial use. Canal transportation remains
suitable for bulk cargoes that are not required quickly, and it
brings with it the added advantages of keeping heavy traffic off
congested roads and minimising the carrier’s carbon footprint:
Of the four principal transport modes, water is by far the least
damaging to the environment. A 12 barge train operating on the
Grand Union Paddington Arm in the 1950s, for example, could carry
over 700 tonnes of freight whilst producing less than 3% of the
carbon emissions of the 30+ road vehicles it replaced. Even a
single 70 tonne capacity barge produces less than 25% of the
equivalent road vehicle emissions when carrying heavy loads such as
aggregates and less than 15% when carrying low density loads such as
waste.
British Waterways: seventh report of session
2006-07, Vol. 2.
An example was the freight contract between British Waterways and
two aggregates companies ― Hanson and Harleyford ― to transport
450,000 tonnes of sand and gravel by barge from a gravel pit at
Denham, through Uxbridge to a canal-side concrete mixing plant near
West Drayton. Although the two sites are only five miles
apart, it was envisaged that the material would be transported by
road on the highly congested western sections of the M40, M25 and
M4. By using the canal, it is estimated that 46,000 road journeys
were saved by the end of the contract.
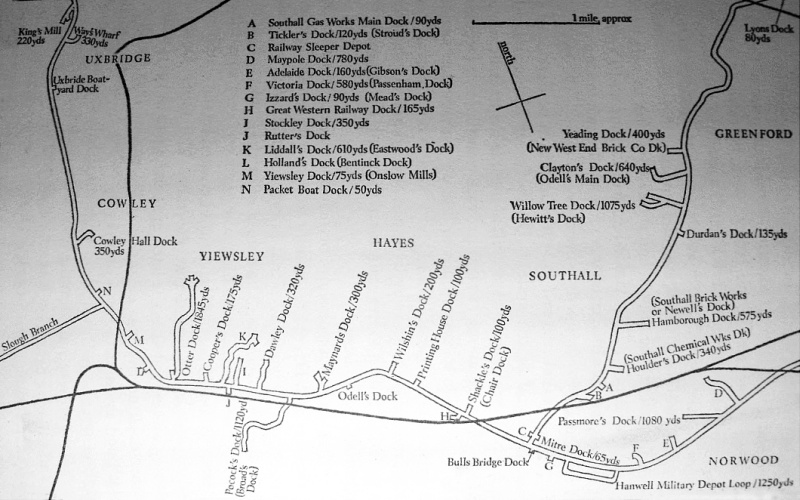
Canal docks and cuts,
Uxbridge to Norwood.
Some 2½ miles south of Uxbridge the canal reaches Cowley lock (No.
89). Here commences the last extended pound [1]
on the main line before it commences its final descent from Norwood
to the Thames. North of Uxbridge the canal flowed mostly
through rural landscape, but from Uxbridge southwards the
surroundings become increasingly industrialized, although there is
some parkland nearing Brentford.
At Cowley Peachey Junction, the Slough Arm branches off to the west.
It was to become an early example of the type of public reaction
against officialdom portrayed in the Ealing Comedy ‘The Titfield
Thunderbolt’, although here applied to the preservation of a branch
canal rather than a railway. By the 1960s, the brickfields and
the sand and gravel pits that the Arm had been built to serve were
worked out and the waterway had become redundant. In keeping
with the fashion of the time, Slough Council planned to convert part
of it into a road. Protest followed, ‘The Slough Canal Group’
was formed, and following a vigorous campaign supported by the local
newspaper (the
Slough Observer) the Arm was reprieved to re-open as a
cruising waterway in 1975. But for some visitors to Slough,
Betjeman’s unflattering judgment remains apt, leaving one to surmise
that a boater’s only motive in navigating this aquatic cul-de-sac is
to seek moorings.

The
entrance to Shackle’s Dock.
Old maps of the Canal ― such as the route maps at the head of this
chapter and those below ― show that many docks and cuts once
left the canal banks, particularly along the main line to the south
of Cowley and the Paddington Arm. Most have long since been
filled in leaving little or no trace of the waterborne commerce they
once supported, which in the Hillingdon area was mainly
brick-making.
Apart from milling, there was no appreciable industry in rural
Hillingdon before the Canal made available the means to transport
deadweight cargoes over distance. This stimulated the
exploitation of the area’s brickearth deposits and during the 19th
Century brick-making grew into a major industry. Eventually
some five million bricks a year were moulded and fired in the local
brickfields, and transported by canal from the numerous docks and
cuts created to serve the industry ― such as Otter, Pocock’s,
Wilshin’s, Printing House, Shackle’s, and Yeading docks ― to a
distribution yard at Paddington Basin’s South Wharf. A good
deal of Victorian West London was built from bricks burnt in clamps
in the locality, the bricks containing household ash brought by
barge from the refuse wharves at Paddington to be mixed with the
local clay.
――――♦――――
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
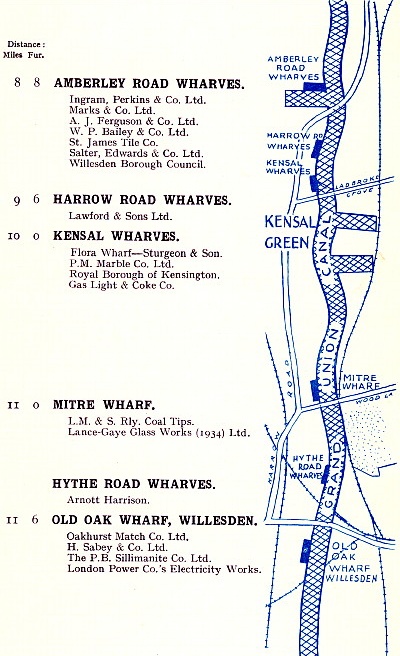
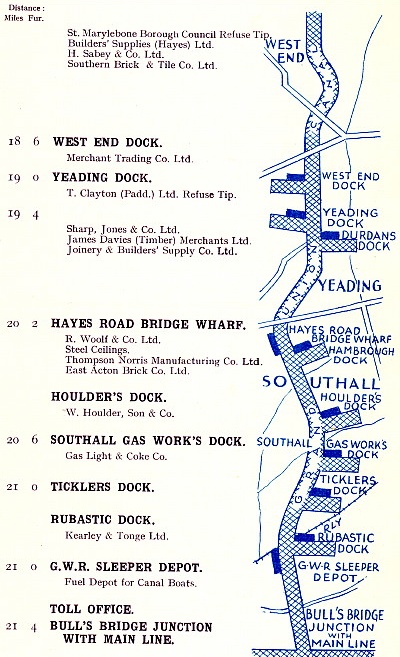
Grand Union Canal route map
(c.1938) showing the wharves and docks that
lay between
St. Pancras, on the Regent’s Canal, and Bulls Bridge. |
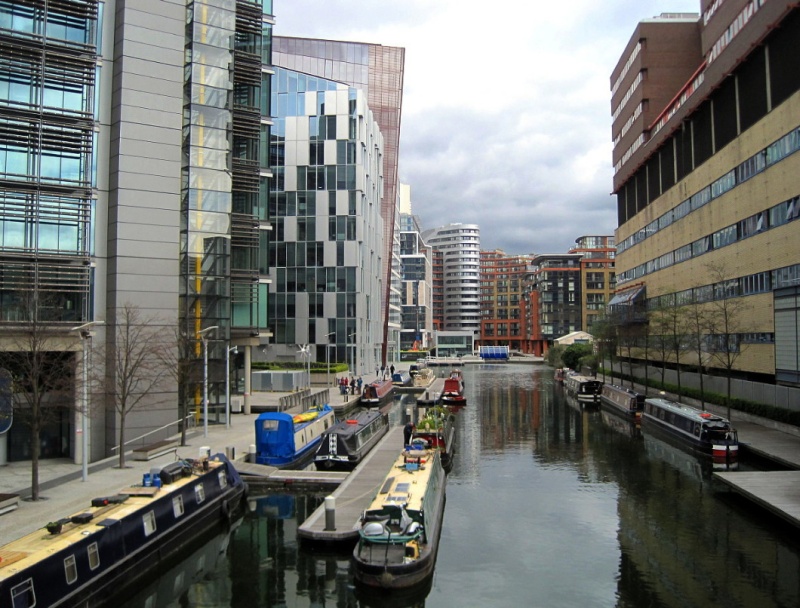

Paddington Basin today ― and in
the 1930s.
The layout
diagram
further down this page shows that the
left-hand wharf was once used for refuse
disposal.

|
 |
|
Map showing
Paddington, c.1790. The Westbourne
(in blue)
flows into Hyde Park's Serpentine lake.
|
Bull’s Bridge Junction is at Hayes, some
two and a half miles south of Cowley Peachy. Here commences
the Paddington Arm, which initially heads off in a
northerly-easterly direction before describing a clockwise arc to
its destination adjacent to the former Great Western Railway
headquarters at Paddington. Station and canal basin are linked
by a walkway that extends across the station platforms, and also by
Praed Street, so named to commemorate the first Chairman of the
Grand Junction Canal Company; and it was at St. Mary’s Hospital in
Praed Street where, in 1928, Alexander Fleming discovered
penicillin, a breakthrough that revolutionised medicine and earned
him a Nobel Prize.
“Although Paddington is now contiguous to the Metropolis, there
are many rural spots in the Parish, which appear as retired as if at
a distance of many miles. From this place a canal has been
made, which joins the Grand Junction Canal at or near Hayes.
It is now finished, and there are noble wharfs for Staffordshire
coal, &c. At the Basin, a passage boat to Greenford Green, and
Uxbridge, sets off daily during the summer months at eight o’clock
in the morning: a breakfast is provided on board, and other
refreshments may be obtained. The terms are reasonable, viz.
five miles for a shilling, ten miles for eighteen pence, and the
extent of this still voyage to Uxbridge may be enjoyed for
half a crown . . . . about three miles west from the Basin, is the
Mitre tavern, situate on the bank of the canal, opposite to a spot,
once of pugilistic note, called Wormwood Common, or more generally
Wormwood Scrubs . . . . A pleasure boat is established by the civil
and attentive landlord of the Mitre, which leaves the Basin of the
canal early in the afternoon, and returns at a reasonable hour in
the evening: in this rural place of accommodation, the refreshments
are excellent.”
A Pocket Companion for the tour of London and its
Environs (1811) |
Looking back at the success of the Paddington Arm, it is surprising
that a branch canal into London was not considered an essential part
of the original scheme, but no such application was included in the
canal Bill placed before Parliament in 1793. It was not until
the following year that Jessop and Barnes surveyed a route.
Paddington was probably selected as the terminus due to its location
on the outskirts of the expanding Metropolis, with good access to
the City via the ‘New Road’, [2] while the line
from Bull’s Bridge was free from the need for locks or substantial
engineering. Indeed, the only challenges were to cross the
River Brent near Alperton and the Westbourne near Paddington, both
requiring significant embankments across the respective river
valleys, the rivers being bridged by short aqueducts. [3]
Maps of the period show Paddington as a village on the edge of the
approaching city, while to its west the Westbourne (also known as
the Westbrook and the Serpentine) meanders into the Serpentine lake
in Hyde Park. When Belgravia, Chelsea and Paddington were
developed, it became necessary to divert this river into culverts in
order to build over it, work that was completed in the 1850s.
Since then, the Westbourne has become one of London’s lost rivers ―
in fact, part of its sewage system.
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Extract from the
Preamble to the Act
authorising
the Paddington Arm
(35 Geo.
III. C. 43 1795). |
The Company obtained the necessary Act in
1795, but shortage of funds and a prolonged dispute with the Bishop
of London over the acquisition of land delayed completion of the
Paddington Arm until the 10th July 1801, when it opened to the
public rejoicing that usually accompanied such events (Appendix
II). At that time, the Arm crossed open countryside,
passing only an occasional village, such as Harlesden. Its
terminus at Paddington was described thus:
“At Paddington a spacious basin or straight cut, 400 yards long
and 30 wide, has been formed with wharfs at its head, and others are
daily extending westwards along its sides; behind this, on the north
side, is a spacious yard for a vegetable and a hay and straw market,
with large sheds, under which loads of those articles can stand in
the dry when it rains; and on the fourth side pens are erected and
provision made for a large cattle market. The number of wharfs
erected on this extensive line and its branches by individuals is
too great for them to be particularized . . . . The market at
Paddington, after an ineffectual opposition from the City of London,
was opened in May 1803 for the sale of fat cattle, hay, straw, corn,
vegetables, &c. . . . In June 1801, packet boats were established,
that continue to pass regularly at stated hours during great part of
the year, for the conveyance of passengers and parcels between
London and Uxbridge; and for some time after the opening of the
Buckingham branch, a boat went regularly between Paddington and that
town; but the number of passengers and parcels was found inadequate
to support the expense. . . . Mr Pickford has a great number of
boats, which proceed as regularly day and night upon this canal, and
the other canals north of it, as the mail coaches do on the roads,
although with less expedition. A common trading boat has been
known to arrive at Paddington in 63 hours from Coventry.”
The Political State of the British Empire (Vol 3),
John Adolphus (1818)
Much of the traffic in those early years consisted of inbound
cargoes of hay, straw and agricultural produce, with outbound cargoes of manure
and other city waste (used as a crude agricultural fertiliser), but bricks,
sand, gravel and other building materials were to become one the Arm’s staple
cargoes during the years when London was expanding. Sand and gravel pits,
and brick kilns ― fired by coal shipped by canal from the Midlands ―
proliferated at Hayes, West Drayton, Iver and Langley.
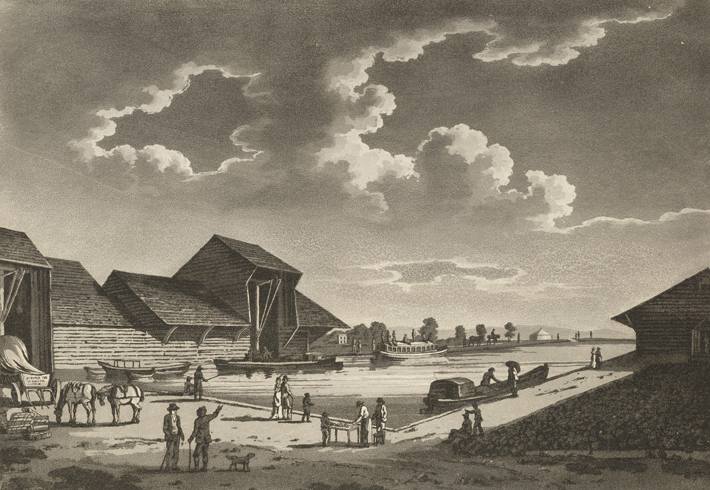

An artist’s
impression of Paddington Basin as built.
――――♦――――

|
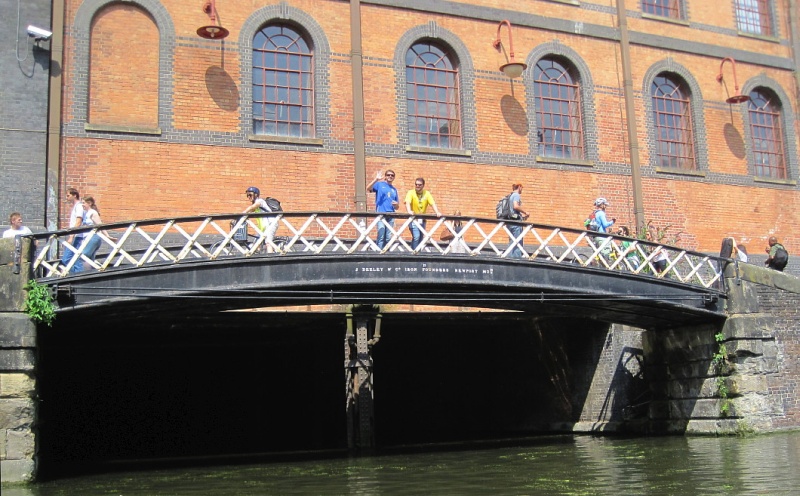
The Regent’s
Canal at Camden ― the London and North Western Railway Interchange
Warehouse.
The
warehouse has a canal basin beneath it, its entrance being spanned
by a fine cast iron towing path bridge (J. Deeley & Co Iron Founders
Newport Mon) dating from c.1846 ― the warehouse (Grade II Listed)
dates from c.1896. Of four storeys topped by handsome
chimneys, its multi-coloured stock brick walls with blue engineering
brick dressings, cast-iron windows with small panes and a modular
pattern of repeating window bays, combine to give the building a
strong period industrial character. |

When the Regent’s Canal was finally completed in 1820 ― it opened in
two stages due to its construction costs being seriously
underestimated ― it extended the Paddington Arm around the City to
the Port of London. As a consequence, Paddington Basin lost
much of its business to new wharves and docks that were better
placed for the delivery of goods to customers’ premises:
“At its first opening, passenger boats went about five times a
week from Paddington to Uxbridge; and the wharves at Paddington
presented for some years a most animated and busy appearance, on
account of the quantity of goods warehoused there for transit to and
from the metropolis, causing the growth of an industrious population
around them. But this was only a brief gleam of prosperity,
for when the Regent’s Canal was opened, the goods were conveyed by
barges straight to the north and eastern suburbs, and the
wharfage-ground at Paddington suffered a great deterioration in
consequence.”
Old and New London: Volume 5 (1878)
In particular, much of Paddington Basin’s prosperity was captured by
the new basin at City Road:
“At the wharf of Messrs. Pickford and Co., in the City Road, can
be witnessed, on a larger scale than at any other part of the
kingdom, the general operations connected with canal traffic.
This large establishment nearly surrounds the southern extremity of
the City Road Basin. From the coach-road we can see little of
the premises; but on passing to a street in the rear we come to a
pair of large folding gates opening into an area or court, and we
cannot remain here many minutes, especially in the morning and
evening, without witnessing a scene of astonishing activity.
From about five or six o’clock in the evening waggons are pouring in
from various parts of town, laden with goods intended to be sent
into the country per canal. In the morning, on the other hand,
laden waggons are leaving the establishment, conveying to different
parts of the Metropolis goods which have arrived per canal during
the night.”
From
The Penny Magazine (1842)

Barges being towed
through Regent’s
Park during the 1930s
― the first two carry coal, the third appears to be timber.
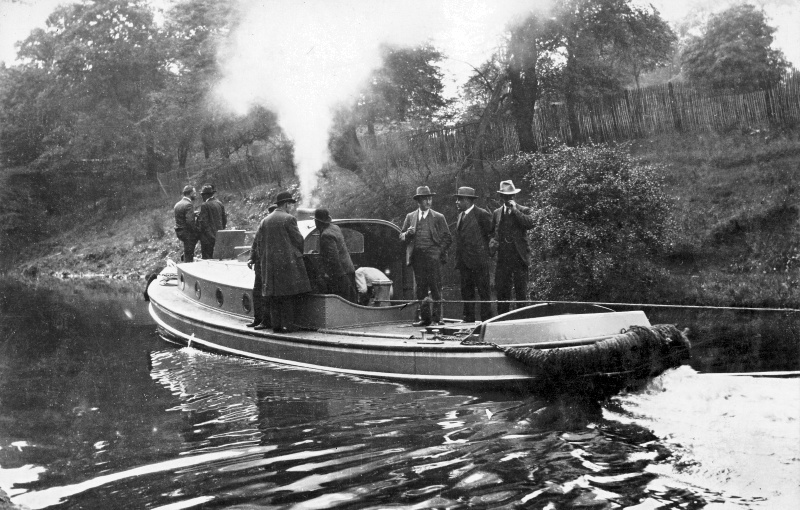

The tug Brent ― built by
Bushell Brothers at Tring in 1928 ― undergoing trails on the
Regent’s
Canal hauling three 90-ton barges.
Photos courtesy of Miss Catherine
Bushell.
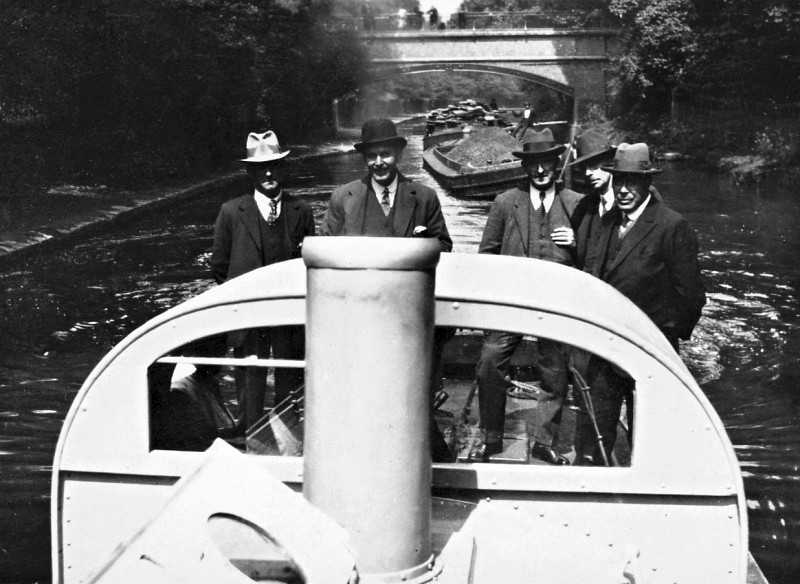

Even though trade on the Regent’s Canal had begun to decline by the
late 1930s, City Road Basin continued to do a substantial amount of
business . . . .
“There is much activity at City Road basin, which adjoins the
City Road, where there are numerous wharves at which are handled
timber of all classes, harvesting machinery, coal, waste paper and
chemicals. A feature of the Basin is the depot belonging to
Messrs. Fellows, Morton and Clayton Ltd., from which a daily service
of motor-driven barges operate.”
Grand Union Canal Company
advertising material, c.
1938
. . . . and the Canal in general remained busy, although closure of
the small power stations it serviced following Battersea A coming on
stream during the mid-1930s resulted in a considerable reduction in
its coal traffic:
“Traffic on the Regent’s Section can be divided into two
categories. First there are canal boats which receive their
cargoes from steamers in the Regent’s Canal Dock and other
London docks, and proceed up the Grand Union Canal to the Midlands.
Secondly, there is the barge traffic which comes in from the River
Thames, or receives cargoes from ships in the Dock destined for
wharves in the London area. Hundreds of thousands of tons of
merchandise pass along this section of the Canal, comprised chiefly
of coal, timber, straw-boards, iron, building materials and oils.”
Grand Union Canal Company
advertising material, c.
1938

|
An interesting view
of the Regent's Canal showing the construction of the London &
Birmingham Railway in progress in May, 1837. This view shows the
bowstring bridge ― probably designed by Charles Fox (later Sir) ― on
the Euston extension. The drawing is one of the series of the
railway under construction, by John Cooke Bourne. |
――――♦――――

|
Layout of
Paddington Basin in 1891 ― the Hay & Straw Store survives as
offices. Large amounts of refuse were shipped from the refuse
wharves, much of it being used to fill worked out pits and redundant
docks. An account of this unsavoury business is given at
Appendix III. |
Considering the damaging impact that railways were to have on the
canal system, it is ironic that the opening of Brunel’s Great
Western Railway terminus at Paddington in 1838 led to Paddington
Basin regaining some of its former importance as a transport
interchange. By the late 1930s, Paddington Basin still had
seventeen tenants, including Shell Mex and wharves for the borough
councils of Paddington and St. Marylebone, from which:
“Large quantities of parish refuse, collected from the
neighbouring districts, are loaded onto craft in Paddington Basin,
and disposed of at various points on the Long Level. Sand from
Leighton Buzzard, and building materials from other points on the
Canal, are brought by canal boat into Paddington Basin for
distribution by lorries to all parts of London. Timber and
iron from steamers in the River Thames is also dealt with in the
Basin.”
Grand Union Canal Company
advertising material, c.
1938
The Paddington Arm had been a catalyst for the development of
north-west London, with many businesses realising its transport
potential, including the inevitable gas works (at Southwell and
Kensal) ― large consumers of coal and exporters of coke and tar ―
and businesses dealing in timber, glass, cement and tiles. At
Kensal Green:
“. . . . is situated another of the Gas, Light and Coke Company’s
stations, coal for which is brought by canal barge from steamers
discharging in the Regent’s Canal Dock. In addition,
large quantities of coal are brought from the London, Midland and
Scottish Railway, whose tips are at Mitre Wharf . . . . Another
electricity station of the London Power Company is situated at
Willsden, and is supplied with coal conveyed by canal boats from the
several Warwickshire collieries.”
Grand Union Canal Company
advertising material, c.
1938
|
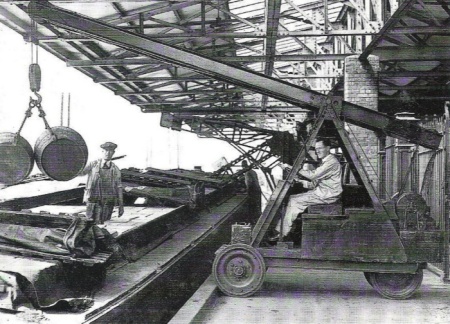 |
|
The
Heinz wharf at Harlsden |
In its later years, household names such
Heinz, J. Lyons, Glaxo, Rockware Glass and Guinness built factories
and wharfs on its banks.
Built in 1925, the Heinz factory was located at Harlsden on a
20-acre site, but owing to the demand for its tomato soup, baked
beans (which had previously been shipped from North America) and a
range of other food products, the site eventually more than doubled
in size. Its long canal frontage permitted loading bays to be
built to handle the raw beans and tomato puree that arrived by barge
from the London docks, and to export finished goods by the same
route. The firm ceased using canal transport in 1967.
Despite major investment in the factory, the growth of supermarket
own-brand products and the harsh economic climate of the 1980s led
to a decline in business, and the Harlsden plant closed in 2000.
The Guinness brewery at Park Royal was situated on the Paddington
Branch southeast of Alperton, a canal-side location that enabled the
firm to manufacture its product close to market, while being able to
obtain a large brewery site at relatively low cost. Guinness
relied on the Canal for transporting its barrels of stout into
Paddington for distribution to its London outlets, also further
afield to the Grand Union Canal Company’s distribution centre at
Sampson Road wharf in Birmingham. Empty barrels were carried
in return. To maintain the Birmingham run’s tight schedule,
the boats were four-handed to allow the crews to complete the round
trip in a week. But the exceptionally heavy winter of 1946-47
froze the Canal, bringing traffic to a standstill for many weeks,
and Guinness transferred their distribution to road transport.
At Greenford, a glass works was opened by W. A. Bailey in 1900 to
exploit the Canal’s location. Not only did the Canal provide
transport for the bulk materials needed for glass making, it also
provided smooth transport for the fragile goods produced. The
company was later incorporated within the Rockware Glass which, in
1919, also redeveloped the site of an adjacent white lead works, the
Purex Lead Company, which had been used for munitions production
during the WWI. Rockware’s Greenford factory stood on the
south side of the Canal and remained in production until 1973.
|
 |
|
The
dock of J. Lyons at Greenford. |
J. Lyons Ltd. had their factory at Greenford. Opened in 1921,
at its peak the factory employed 300 people. Lyons equipped their canal
dock with the latest cargo-handling facilities enabling several barges to be
discharged simultaneously. Their consignments were stored under excise
control before being released for use in tea blends, coffee, confectionery and
grocery lines (tomato sauce, salad cream, jellies, custard powder and mixes).
So proud was the firm of their dock and warehouse that they were proudly shown
to the King and Queen during a royal visit in 1923.
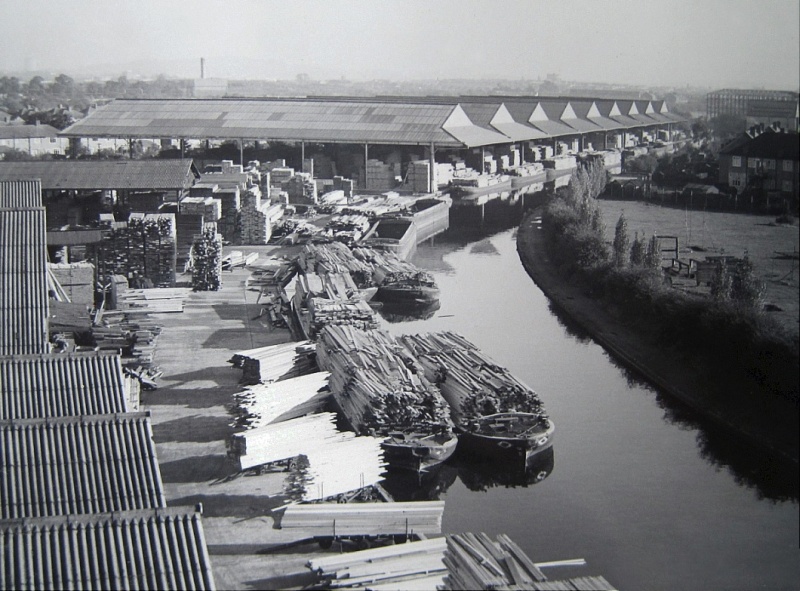

Hayes Bridge Wharf and the yard of James
Davies (Timber) Merchants Ltd.
Some of the barge names and
owners are listed at Appendix IV.
|
 |
|
The
Nestlé factory at Hayes. |
Many factories such as these were built
close to the Canal because they ran heat-dependant processes, such
as brewing, malting, food preparation, brick, tile and glass making.
In an age before oil, gas and electricity became economic
alternatives for heating, their boilers were fired with coal, which
was transported cheaply by canal from the Midland collieries.
One such customer was the Nestlé factory at Hayes, known to boatman
as the ‘Hayes Cocoa’ after its former owner, the Sandow Cocoa
Company. For many years the factory received regular
consignments of coal by canal until eventually it converted to oil
fired boilers, and the last load of coal was delivered from Cannock
in 1959. Visually, the factory’s canal frontage has nothing to
recommend it, but its main entrance ― facing away from the Canal ―
is an attractive piece of Art Deco. A Wallis Gilbert creation,
it is framed with trees and set back behind lawns with massive
railings and gates imported from the company’s main works in
Switzerland. Wallis, Gilbert and Partners were responsible for
the design of many buildings in the Art Deco style during the
inter-war years, their best known creations being the Hoover Factory
on Western Avenue, Perivale (1931-1938), and the Victoria Coach
Station (1931-32).
Another regular customer for
canal-delivered coal was the firm of Kearley & Tonge, later to
become International Stores and one of the first modern supermarket
chains. Known as the ‘Jam Ole’ to boatmen, the factory’s coal
shipments were landed at Rubastic Dock (now filled in) on the
Paddington Arm from collieries around Atherstone on the Coventry
Canal. International Stores (since absorbed into the
Somerfields empire) was immortalised together with two other
long-forgotten grocers in a verse from John Betjeman’s poem
Myfanwy:
|
“Smooth down the Avenue glitters the bicycle,
Black-stockinged legs under navy blue serge,
Home and Colonial, Star, International,
Balancing bicycle leant on the verge.” |
Kearley & Tonge opened their jam and marmalade factory at Southall
in 1913, later extending their business into a wide range of food
products. The Jam Ole Run ― some 246 miles and 194 locks ―
could, under the most favourable conditions, be completed in seven
days. Time was important, for the crews were paid by tonnage
and the quicker they arrived to unloaded, the quicker they could
return for another load. But by the late 1960s the Jam Ole was
struggling and the last cargo of coal, from Baddesley Colliery at
Atherstone, was delivered in 1970, [4] so ending
nearly two centuries of carrying coal to London by canal:
“I had a real nice stone jam jar from the Jam-’Ole. You
went right in and under the bridge to deliver coals at the Jam-’Ole.
It had its own big basin, tooked two pairs of boats and two big
barges. All gone now, just cars were the water used to be.
They used to be everso perticler at that jam factory, one little
chip in a jar, out it were throwed on their roobish ’eap. We
used to ask if we could have it, specially if it were one of them
deep-blue and some stone ones. Crammed with flowers on yer
cabin top you never noticed no chips. Lovely!”
Ramlin Rose by Sheila
Stewart, Oxford University Press (1994)
――――♦――――
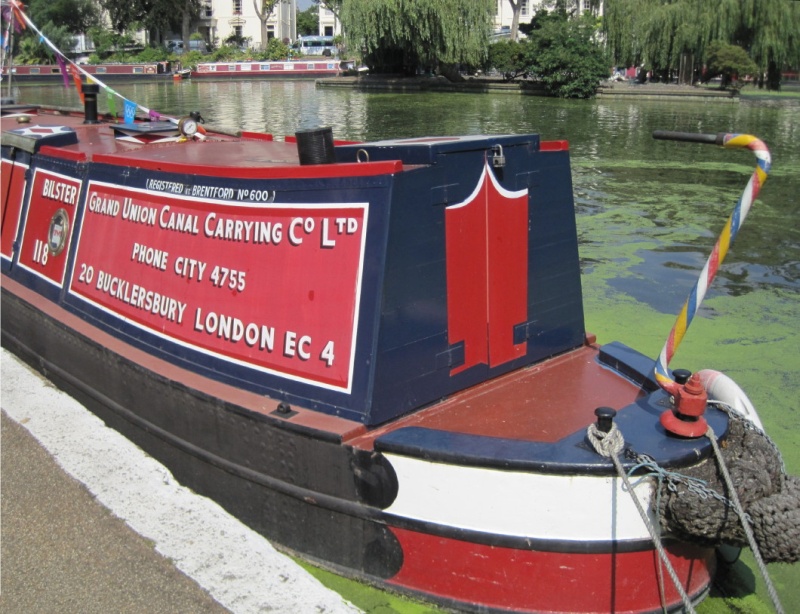

Before leaving Bulls Bridge Junction, a further once-important canal
tenant needs to be mentioned. This was the Grand Union Canal Carrying
Company, which following nationalisation in 1948 was absorbed into British
Waterways’ carrying fleet. [5]
The Grand Union Canal Company’s carrying subsidiary was formed in
1934, and Bulls Bridge Junction became the location of its slipways, repair yard
and traffic control office. [6] A recess in the canal bank of
a couple of hundred yards in length, was built as a lay-by where boats awaiting
instructions could tie up, end-on, without obstructing the channel.
Photographs of the period show the lay-by tightly packed with empty narrow boats
moored by their sterns to iron rings set into the concrete wharf, the boatpeople
occupied with polishing their brassware, hanging out their washing, refuelling
or just relaxing over a pipe of tobacco while their children played on the
wharf.
The role of the traffic control office was to accept orders and
allocate shipping instructions to boat crews. It also kept track of the
location of each boat and its activity by means of positioning coloured discs on
a large wall-mounted network diagram (Appendix
V). By repositioning the discs
on receipt of telephoned daily updates, it was possible to identify slow-moving
and stationary boats, as well as estimate what carrying capacity would be
available at any loading point, and when. In this way the fleet was
managed, no mean achievement in the days before cell phones.
 |
|
School barge Elsdale. |
Bulls Bridge depot also hosted a five-bed maternity unit [7]
and a school. The school was opened at Rickmansworth in 1930
for the benefit of boatmen’s children, but later moved to West
Drayton and finally to Bulls Bridge. Housed on a barge
provided by the Company, the
Elsdale could take about 40 children who were provided with
brief periods of education while their parents were awaiting orders.
By 1939 the Elsdale had become unsound and was hoisted onto
the canal bank where schooling continued alongside the depot
buildings until the 1950s.
By the end of WWII., canal carrying was in terminal decline.
Although some independent carriers soldiered on until the 1970s, the
business’s financial losses coupled the harsh winter of 1962-3, when
the canal system was iced over for many weeks, caused British
Waterways to cease its carrying operations. Today, the Bulls
Bridge depot hosts a Tesco supermarket and car park, but one of the
Carrying Company’s dry docks has been retained as a memento of a
bygone trade while the lay-by is now home to an estate of strikingly
odd-looking house boats.
――――♦――――
South of Bulls Bridge the Canal continues through an industrialised
area, but very few of the many wharves, cuts and docks from the
Canal’s commercial era survive, for having fallen into disuse they
were filled in with London’s refuse, shipped, ironically, by canal
from Paddington.
The Ordnance Deport at Weedon Bec was not the only gunpowder
magazine to be served by the Canal. In 1811, the government
decided to replace the old powder hulks [8] moored
in river estuaries with permanent storage facilities. Four new
magazines were built, one being on a 47 acre site on the Canal at
North Hyde. Acquired in 1813, the site was originally planned
to connect to the Canal via a branch that would also form a
defensive loop, in contrast toWeedon Bec, which was surrounded by a
high wall with sentry posts. For some reason the plan for a
moat was abandoned, and what resulted was an extensive branch canal,
most of which ran parallel to the main line, and from which six
docks extended at right angles. A barracks building was
erected that could accommodate three officers and 50 other ranks,
and mounds were built on the site to deflect the blast should there
be an explosion. Gunpowder was shipped in government-owned
barges that entered the site through a 14ft wide stop-lock.
The North Hyde Ordnance Depot had a short life, being sold by
auction in 1832. A contemporary newspaper advertisement stated
that it comprised:
“. . . . an entire frontage of about 2,500ft to the Grand
Junction Canal with which the Ordnance canal on this land has direct
communications. The extensive and valuable magazines, mixing
houses, cooperages, boat houses, watch houses and other buildings
standing upon this lot . . .”
The Times, 5th March,
1832
Also put up for sale were the barracks, parade ground, a “capital
dwelling house” (formerly occupied by the Ordnance Storekeeper)
and “ten cottages, with a garden to each, occupied by the foreman
and labourers”. Following the sales, the barracks building
became an orphanage and the branch canal a wharf to a brick works ―
in which the working conditions of the children it employed were
grim. A police officer stationed at North Hyde stated that
those who worked there were:
“. . . . very rough in manner and coarse in language, and
terribly given to drink, but I have always found them honest and
reasonable to deal with; . . . . I often wonder that the children
can stand the work as they do, but nothing seems to hurt them; they
are as hardy as ground toads, as the saying is; yet I have seen them
so tired at the end of the day’s work that the men have had to take
them up in their arms to carry them home.”
Children’s Employment Commission – Brickfields,
1866
――――♦――――
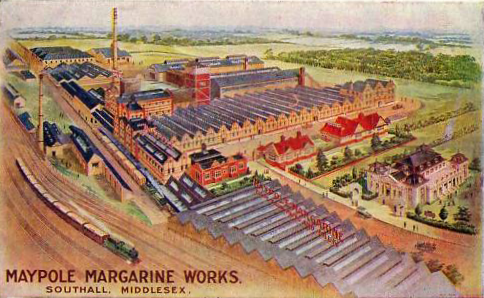
By the 1930s all trace of the military depot and its canal had been
obliterated, but a nearby private canal branch that has managed to survive is
the Maypole Dock. Described by its current owners as a
“community of moorings with gardens”, in its heyday it served
one of the largest margarine factories in Europe.
In 1869, the French Emperor, Napoleon III, offered a prize to anyone
who could make a satisfactory substitute for butter, suitable for use by the
armed forces and the lower classes. The French chemist Hippolyte
Mège-Mouriès invented a substance he named ‘oleomargarine’, which quickly became
shortened to ‘margarine.’ In 1894, Otto Monsted, a Danish margarine
manufacturer, built a large factory at Southall to manufacture this ‘poor man’s
butter’. Named the Maypole Dairy, it eventually became one of the largest
margarine manufacturing plants in the world, occupying a 68 acre site that
included its own covered canal dock. The Maypole Dairy Company (later
acquired by Unilever) closed in 1925, apparently due the prohibitive cost of
altering production from barrels to pre-packaged cartons. [9]
Much of the site was sold off, one later tenant being Quaker Oats who opened its
works in 1936 to produce cereals, pig, and poultry foods, the grain being
shipped from the docks mainly by canal. Jack Gaster, a Thames boatman,
recalls taking cargoes to Maypole Dock shortly after the outbreak of WWII:
“. . . . the job I liked most was being Wharf Bosun up on the
Grand Union Canal at Southall where I was responsible for delivering
canal barges to Messrs. Poulton & Noel [10]
laden with Navy beans to be turned into baked beans. I used to
collect the craft from Brentford Dock and tow them up to Southall
behind a horse; there were a number of locks to negotiate including
the Hanwell Flight. This was a series of seven locks one after
the other and needed a little skill in controlling the barge in
order to prevent damage to the lock gates. Once these had been
negotiated and the craft were safely in the Maypole Dock, it was a
matter of uncovering and removing the hatches and leaving the work
force to remove the beans. The dock was roofed over so that
there was no need for my presence until it was time to bring the
barge away and return it down to Brentford Dock for return to the
river.”
WWII People’s War, BBC
――――♦――――
|
 |
|
Turner’s post mill at Southall. |
A short distance from Maypole Dock the
Canal reaches Norwood top lock (No. 90), which marks the beginning
of the its final descent to Brentford and the River Thames. In
this section the canal enjoys a brief respite from the industrial
landscapes of Uxbridge and Hounslow as it skirts the perimeter of
Osterley Park before completing its journey at Brentford, once a
busy river port, which was also served by a competing branch of the
Great Western Railway.
The construction of the Great Western and Brentford Railway
Company’s branch line gave birth to ‘Three Bridges’ ― or ‘Windmill
Bridge’ as it is referred to locally ― a rare example of a triple
crossing in which a road (Windmill Lane) crosses a canal aqueduct
which crosses a railway, all at the one point. Brentford Dock
and its branch railway are generally considered to be Isambard
Kingdom Brunel’s last significant engineering project, being
completed shortly after the great engineer’s death in 1859.
The construction of a branch line southward from Southall to
Brentford Dock required the Canal to be crossed at a point where it
was already crossed by Windmill Lane. Brunel’s solution was to
drive a cutting for his broad gauge railway beneath the canal, which
he placed in a cast iron trough, while a new cast iron bridge was
built to carry Windmill Lane over both.
|
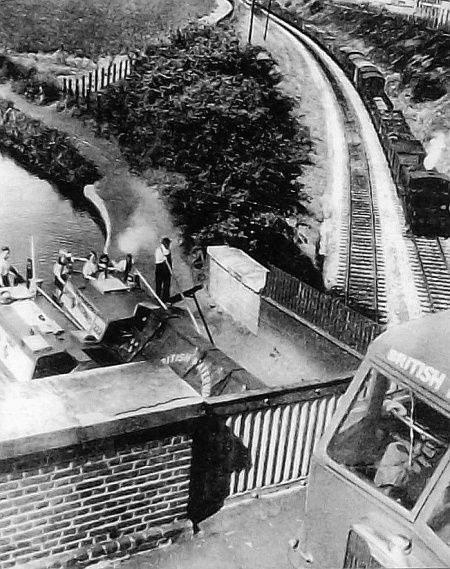 |
|
Three Bridges,
Hanwell ― the Canal crosses the railway
in an 8 ft-wide
cast-iron trough
aqueduct. |
As the name of the lane suggests, this
engineering oddity stands near the spot where a windmill once stood
and which attracted the attention of a local Brentford artist,
Joseph Mallard William Turner. Turner exhibited ‘Grand
Junction Canal at Southall Mill, Windmill and Lock’ in 1810, his
painting depicting a post mill, its sails at rest and a pair of
millstones leaning against its roundhouse wall. In the
foreground a narrow boat is locking up, two men pushing hard against
the balance beams of the lock gates while canal horses graze idly on
the canal bank in this idyllic scene. The lock is thought to
be Hanwell top lock (No. 92), the bridge in the background being
that which carried Windmill Lane across the Canal.
The Great Western Railway branch line
through Three Bridges once terminated at Brentford Dock, [11]
which lies adjacent to and slightly upstream of the point at which
the canalised River Brent enters Brentford Creek to join the Thames.
Brentford Dock was constructed between 1855 and 1859 to a plan by
Brunel. The dock, which was served by a large railway
marshalling yard, warehouses, workshops and goods sheds, was
designed as a transhipment terminal for traffic carried by barges
and lighters from the London docks, the Great Western Railway and
the Grand Junction Canal. Through most of its existence it was
a commercial success, the traffic it handled including coal, steel,
timber, wood pulp, flour, animal feedstuffs, cork and general
merchandise. But by the 1960s, the development of the motorway
network and its greatly increased use for road haulage took traffic
away from the Thames, and Brentford Dock gradually fell into disuse.
The dock closed in 1964 and the site has since been redeveloped with
housing and a marina.
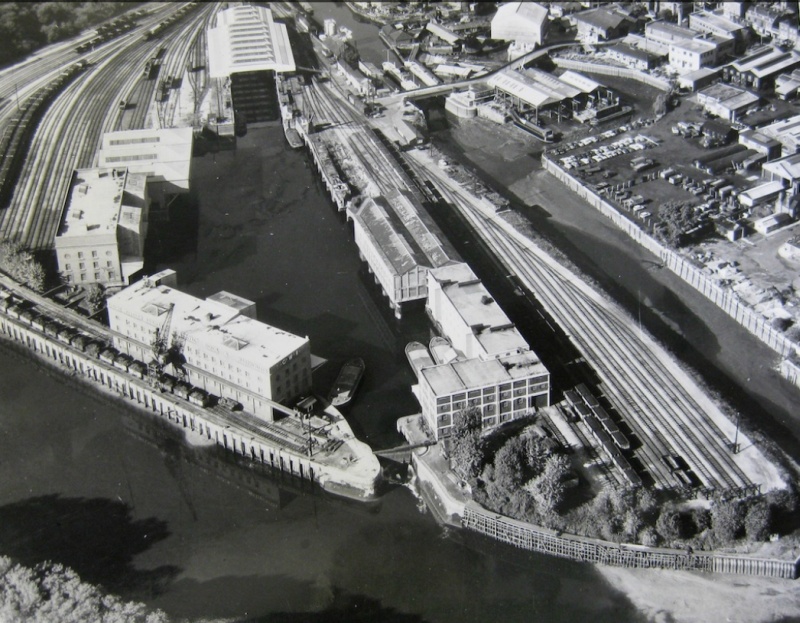
Brentford Dock. Brentford Creek,
leading up to Thames Lock and the start of the
Grand Junction Canal, is on the right of the picture.
――――♦――――
Just to the east of Three Bridges commences the Hanwell flight of
six locks that lower the canal by just over 53 feet within a third of a mile.
Along this section runs a high brick wall behind which were the extensive
grounds of what was once the County Asylum, now Ealing Hospital. A
bricked-up entrance shows where boats once passed into what the boatmen called
‘Asylum Dock’ to deliver coal for the boilers and take away fruit, vegetable and
animal produce cultivated by the inmates in the Asylum’s large market gardens.
For its time, the medical regime took an enlightened attitude to the care of
their patients by encouraging the use of their skills and trades. This
‘therapy of employment’ benefitted both the Asylum and the patients, and was a
precursor to what we know as ‘occupational therapy’.
 |
|
The
Company’s steam inspection launch ‘Swift’ descending the
Hanwell flight. |
An old enemy of canal transport, ice. These pictures are of
the Canal at Hanwell during the winter of 1962-63.
.JPG)
The former County Asylum lay behind the imposing wall on the towing
path bank.
.JPG)
.JPG)
At Hanwell bottom lock (No. 97), the Canal flows into
the River Brent:
|
“Gentle Brent, I used to know you
Wandering Wembley-wards at will,
Now what change your waters show you
In the meadowlands you fill!
Recollect the elm-trees misty
And the footpaths climbing twisty
Under cedar-shaded palings,
Low laburnum-leaned-on railings
Out of Northolt on and upward to the
heights of Harrow hill.” |
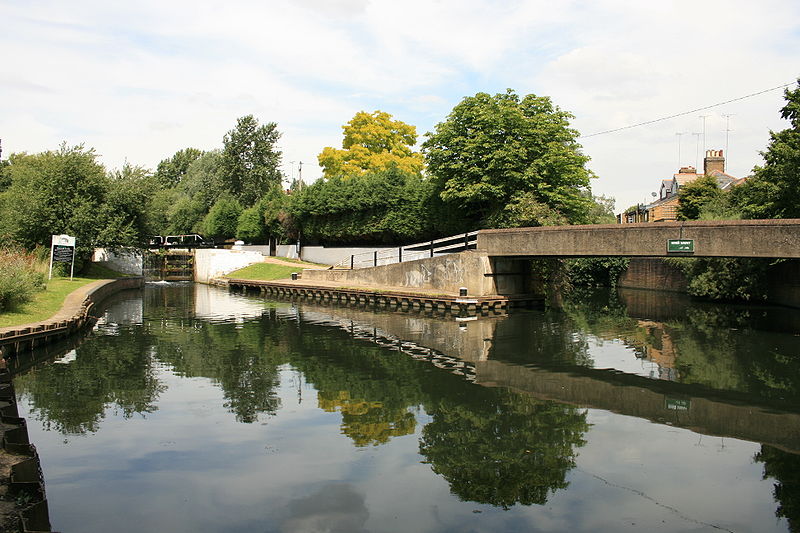

The Canal flows into
the River Brent at Hanwell bottom lock, which becomes a canalised river.
So wrote the late Poet Laureate, Sir John Betjeman, of the River
Brent as it flowed towards Brentford and the Thames. Much of the river
north of this point has since been driven underground by the suburban growth of
London or corseted in concrete as a flood protection measure. The risk of
flooding here is real, and it came to pass in 1841.
Some 6 miles to the north of Brentford lies the Brent Reservoir.
Built by the Regent’s Canal Company in 1835 to address a water shortage on the
Paddington Arm and the Regent’s Canal, the reservoir straddles the boundary
between the London boroughs of Brent and Barnet. Early in the morning of
the 17th January 1841, a sudden thaw following freezing weather caused the
reservoir to burst its earth wall. A disastrous flood then swept down the Brent
into the Canal to descend on Brentford, ripping barges from their moorings and
leaving much destruction in its wake . . . .
“. . . . a few minutes before four o’clock a loud noise was heard
to the north of the town, which momentarily approached nearer and
nearer; and it was soon ascertained that the narrow stream of the
Brent had swollen into a mighty river, and overflowing its banks,
was pouring itself into the already increased waters of the canal.
Numbers of boats, barges, and lighters, were instantly torn from
their moorings, and driven with great force through the bridge,
towards the Thames. At the same instant, also, the accumulated
waters having overflowed all the premises north of the high road,
burst with frightful force through two avenues by the houses . . . .
It is impossible to describe the scene at that moment. Men,
women, and children, many of them in their night clothes, were
running in all directions for places of shelter, while the roaring
of the water, added to the screams of the terrified inhabitants of
the boats, and of the individuals inhabiting the numerous cottages
running south of the town down to the water side, were most
appalling. In a very short time, all the houses at that portion of
the town were flooded . . . . five large barges were driven by the
force of the water against the wharf of Mr. Fowler, an extensive
wharfinger at Brentford-end, and swamped, some lying over others. .
. . but it was nearer to the mouth of the outlet of the Thames that
the greatest damage was done, and a scene of shipwreck unparalleled
so far inland presented itself. The spot in question is at the
bottom of the Boar’s Head yard, a turning leading from the high
road, nearly opposite to the market-place, down to the canal.
Off this spot the canal passes through some meadows, and there is a
foot bridge across it, and near that bridge were piled up craft of
various descriptions to the number it is said of fifteen.
There would no doubt have been more, had not the pressure of the
water forced down a large portion of the wall of the grounds of the
duke of Northumberland, by which the pent-up water obtained an
outlet, carrying with it four or five barges. Some of these
vessels were topsy-turvy, others were on their sides, and portions
of five could he distinctly seen above the water, piled on the top
of each other.”
The Annual Register,
1841
Despite the scene of destruction painted by the press reports of the
time, the loss of life was surprisingly small, with two deaths
reported.
――――♦――――
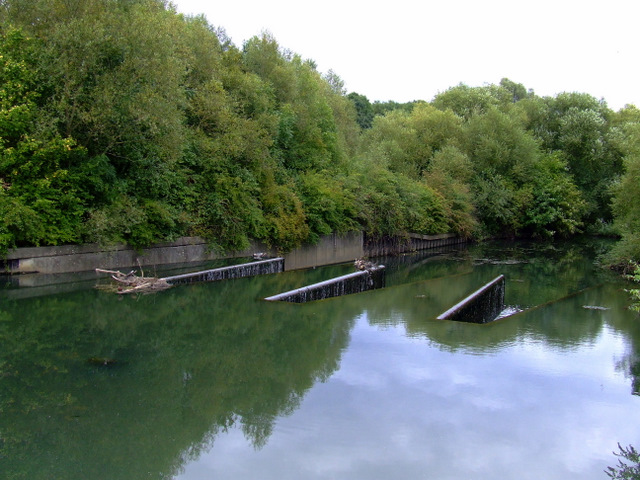

This bypass weir at Osterley Lock is one of
a number that
regulate the depth of the
canalised River Brent.
The River Brent with its weirs and mills was probably unnavigable
until work started on the Canal in 1793, which, apart from its wider bends,
canalised the River along the south-western boundary of New Brentford.
Here, the scenery returns briefly to parkland as the Canal skirts the estate of
Osterley House, an elegant eighteenth century neo-classical mansion by Robert
Adam, now in the care of the National Trust. The scenery is somewhat
blighted by the M4, which the Canal passes beneath before reaching Clitheroes
Lock (No. 99), [12] the last conventional lock on the canal;
the two that remain are electrically operated and are twinned, Thames Lock (No.
101) also being tidal and in the care of a lock keeper. Clitheroes Lock is
but a short distance to Brentford Basin, at the southern end of which is
Brentford Gauging Lock (No. 100). This was the first (or last) lock on the
Canal when it was first opened, and it continues to act as the demarcation point
between the Thames, administered by the Port of London Authority, and the River
Brent/Grand Union Canal, administered by the Canal and River Trust. The
section of Canal between these two locks is semi-tidal due to high tides causing
the Thames to overflow Thames Lock weir back into the Canal.
Brentford Basin was once ringed with wharves and warehouses, and a
hive of commercial activity. [13] Here the transhipment of
cargoes between lighters, river barges and smaller canal craft took place.
Tolls were paid at the Brentford Toll Office based on the weight and type of
cargo, the toll clerk measuring how high a loaded boat was ‘sitting’ out of the
water using a gauging rod to measure the ‘dry inches’ on the side of the boat.
From this could be calculated the toll based on the charge per mile for each
cargo. Although much of this industrial landscape disappeared after the
Canal’s commercial life ended in the 1970s, and is currently the subject of
various regeneration plans, the Basin is not deserted, for many leisure craft
now pass through it. It is ironic to reflect on British Waterways’ view,
published in their house magazine in 1958, that the development of pleasure
boating “will not mean greatly increased earning in the kitty and our main
efforts must always be directed towards getting commercial traffic”.
It was to be another decade before Barbara Castle’s 1968 Transport Act finally
gave official recognition to the recreational value of our inland waterways and
a remit for British Waterways to develop their leisure potential.
.JPG)
.JPG)
|
Pictures of
Brentford Basin during the dreadful winter of 1962-63:
the timber being worked (above and below) was destined for James
Davies (Timber) Merchants Ltd. at Hayes Bridge on the Paddington
Arm. |
.JPG)
Brentford Gauging Lock (No.
100) in the background.
.JPG)
The narrow
boat Nutfield playing tug to a lighter load of timber - the Nutfield
is still around.
――――♦――――
|
 |
|
Boatmen’s Institute, Brentford. |
Before leaving the area of Brentford
Basin, a further point of interest is the former Boatmen’s
Institute. Canal boatmen had a hard and poorly paid existence,
the railways having creamed off their most profitable trade leaving
mostly coal and other low-value deadweight cargoes. Bringing
up families in tiny narrow boat cabins was a struggle and it is
unsurprising, considering the dangerous nature of the trade, that
there was a high rate of mortality, particularly among children.
Few boat people could swim and drowning was not uncommon. Many
canal families were illiterate, their itinerant lifestyle denying
them regular schooling, while access to medical help and to religion
were difficult. Thus, for many the Brentford Boatmen’s
Institute was a beacon where children could be left for weeks at a
time to receive a rudimentary education while their parents carried
loads to Birmingham and elsewhere on the network. The
Institute even had lying-in rooms where women could give birth in
dignity. For one old boatman, the Institute was “the
happiest, blessedest place in Brentford”.
The Institute was designed by local architect Nowell Parr in 1904
for the London City Mission, which had many much larger premises
devoted to sailors in the East End docks. This charming
building is in a redbrick Queen Anne style, with white, rough-cast
upper floors and wide, flat buttresses. For 50 years tea and
compassion were dispensed to the canal community within its walls,
but when canal traffic faded away so did its role in life. The
building became redundant and, at the time of writing, is now a
private dwelling.
――――♦――――

Thames Lock (No. 101) at
Brentford.
The double Thames Lock
forms the boundary between the Thames, administered by the Port of London
Authority,
and the River
Brent/Grand Union Canal, administered by the Canal & River Trust.
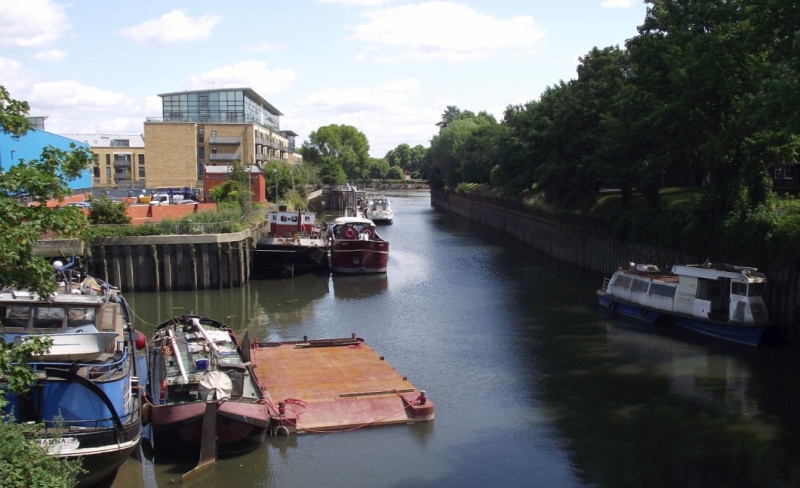

A view in the
opposite direction to that above ― the tidal Brent Creek, with the
River Thames in the distance.
South of Brentford Lock (no. 100), boats had at first to navigate
the tidal Brentford Creek because local millers frustrated its use
to build another lock to enable canal traffic to continue further on
its way. But in 1802, some years after this section of the
Canal had opened, the Company succeeded in building the first Thames
Lock [14] to provide improved access with the
Thames.
Today, the town of Brentford is no longer an important trading
route. Its dock has been redeveloped as a marina surrounded by
flats, maisonettes and houses, while the western side of the canal
basin is currently the subject of planning applications for
redevelopment. Large commercial developments dominate the
Great West Road. But in the eighteenth century, it would
appear, Brentford was an unappealing place; and despite the Turnpike
Trust, the state of the road was extremely bad:
“Though this is called the county town, it is a miserable dirty
place, without a town hall, or any building of that nature . . . .
The road from Hyde Park corner through Brentford and Hounslow is
equally deep in filth, as the road from Tyburn through Uxbridge.
The only passable track of which, during the whole of the winter of
1797-8, was eight inches deep in fluid sludge, the rest of the road
being from one foot to eighteen inches deep in adhesive mud.
Notwithstanding His Majesty travels the road several times every
week there are not many exertions made towards keeping it clean in
winter.”
View of the Agriculture of Middlesex,
John Middleton (1807)
The great lexicographer, Doctor Johnson, took an equally jaundiced
view of the town. So let the last word on this journey from
Braunston to Brentford ― and a judgment that must rank with
Betjeman’s on Slough ― rest with the Doctor:
“I once reminded him [Johnson] that when Dr Adam Smith was
expatiating on the beauty of Glasgow he had cut him short by saying,
‘Pray, Sir, have you ever seen Brentford?’ and I took the liberty to
add, ‘My dear Sir, surely that was shocking.’ ‘Why then Sir,’
he replied, ‘YOU have never seen Brentford.’”
The Life of Samuel Johnson, LL.D,
James Boswell (1791)
――――♦――――
APPENDIX I.
THE KILBURN AQUEDUCT AND EMBANKMENT
“About the year 1798, the proprietors of the Grand Junction Canal
made the Paddington branch of their navigation; its approach to
London rendered two very great and elevated embankments necessary,
one over the River Brent, the other over the valley of the
Serpentine River [a.k.a. the Westbourne], near Westbourn
Green. The first of these embankments was effected by making a
brick aqueduct, of large capacity, under which the Brent passes
generally without much impediment, and which is too far removed from
London to be much dilated upon here; but the latter embankment
essentially interferes with that great object of consideration, the
sewage of the western part of the metropolis. It is formed
over the valley to an elevation of 30 feet above the natural surface
of the ground; a brick aqueduct here, as at the River Brent, being
made for the conveyance of the canal over the Serpentine River or
Westbrook. This brook receives all the waters flowing from the
western side of Hampstead Hill, the south side of Shootup Hill and
Bransbury, Kensal Green, in part, and thence from the eastern side
of the Harrow Road to the bridge at Westbourn Green. This
district being all strong clay, floods, which were frequent before
the embankment, have increased since its formation; no doubt owing
to the limited size of the culvert, the opening being but a little
larger than the old bridge was on the Harrow Road, which has since
been rebuilt on account of want of dimensions. What evil might
arise from the effects of a very sudden thaw cannot easily be
foreseen; because, if the embankment were to be ruptured so as to
let out the waters of the canal, which is for 18 miles without a
lock, they could not be stopped, although there are stop-gates at
the bridges, for they could not be made to act if there were any
great thickness of ice in the canal.”
Some account of the proposed improvements of the
western part of London (1814) – pp.60-61.
The author of this piece may have been aware of the problems
experienced with the Cosgrove embankment and aqueduct. The
aqueduct referred to here is the Kilburn Aqueduct. Sited where
the Canal crosses the Westbourne Valley, the aqueduct still exists ―
approximately where the footbridge west of Little Venice crosses the
Canal today ― but lies buried beneath London’s later development
(and at any rate who would want to live next door to an open
sewer?). In appearance, the aqueduct was probably not
dissimilar to that which Jessop designed to support the massive
embankment across the Great Ouse at Wolverton, but in this case of a
single arch. Today the aqueduct still conveys the Serpentine,
now generally known as the Ranelagh sewer.
――――♦――――
APPENDIX II.
OPENING THE PADDINGTON ARM
reported in The Morning Post, 11th July, 1801.
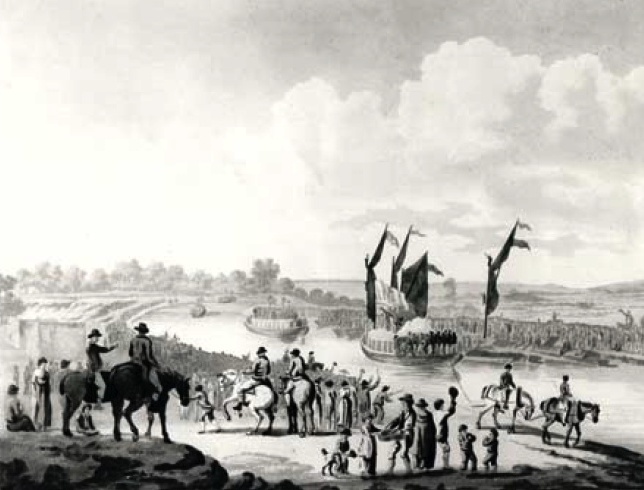

“The canal to Paddington was opened yesterday morning for trade,
with a grand procession along the Paddington Line to Bull’s Bridge
at Uxbridge. Exactly at nine o’clock the Committee, with their
friends, in two pleasure boats, set sail, with colours and streamers
flying, each vessel being towed by two horses. At twelve o’clock the
company were met at Bull’s Bridge by the city shallop (having on
board the Sub-committee of the Thames navigation), and several
pleasure boats, with large parties of Ladies. ― On meeting, a salute
was fired, and then the procession returned in the following order:
1. The Committee and their friends, in two barges, with the
Buckinghamshire band of music.
2. The city shallop.
3. Seven pleasure boats.
At half after five o’clock, the cavalcade reached the Great Dock.
This was announced by the firing of cannon, on
Westbourn-green-bridge, and a volley of musquerry (sic) from the
town. After three huzzas, the company landed, and walked in
procession to the Yorkshire Stinge, preceded by the Buckinghamshire
band, playing ‘God save the King’. At half past six, the company sat
down to an excellent dinner, and spent the evening with
conviviality.
Blue and purple ribbands were worn by the ladies, gentlemen, and men
employed in the concern, on which were written, “The Marquis of
Buckingham, and success to the Grand Union Canal.”
Great praise is due to the Committee for the expedition which they
have used since last spring in completing the canal. A long range of
warehouses are nearly finished for the reception of goods. Yesterday
not less than eight laden barges arrived. A public road, 100 feet
wide, was finished on Monday last to the quay, which is but a few
paces from the Edgware-road.
The day proved as propitious as the undertaking is likely to prove a
prosperous one. The number of persons present could not be less than
20,000; for several miles the banks of the Canal were lined with
people; several stages were erected for accommodation, and a long
string of carriages appeared on the public walk.”
――――♦――――
APPENDIX III.
FILTHY LUCRE
from
GOOD WORDS (Volume 20, 1879)
by
CHARLES CAMDEN.
I HAVE chosen my
title with reference to the nature of the materials from which the
gain of which I have to speak is extracted — very fertile “farms of
two acres,” some of our dingy dust yards prove — not with the
slightest to the character of the extractors. Through the courtesy
of Messrs. W. Mead and Co, I have been allowed to pay a visit or two
to a “contractor’s yard,” which claims to be the largest, at any
rate to do the largest business, in London. It is one of
several bordering the Paddington Basin, which from that circumstance
might be called, by a trade pun, a “slop” basin.
Most of the London dust-yards are at the water-side, for the sake of
the water carriage which the canal or river gives them for their
dust and cinders to the country brick makers.
In Messrs. Mead and Co.’s yard, the electric light is used after
dusk in winter, to enable the men to go on with the loading of the
barges. Wandering along the muddy North Wharf Road, with its
dozens of empty tumbrils resting with their shafts up in the air, or
crossing the canal and railway bridges in Bishop’s Road, you catch
sight of an aurora in the sky, and on entering the yard you see a
big meteor star, pulsing white and bluish white, suspended in
solitary brightness over the black heaps from which the weary
sifters have gone home to rest, weirdly lighting up the men plying
pick and shovel down by the canal, and making part of the sluggish
water seem to be phosphorescently afire. As far at the
influence of the light extends, the separate stones can be
distinguished on the gravel wharf, and within that circle the
lamp-posts and the buildings of the yard stand out clear as by
daylight, or rather clearer, since the mysterious brilliance seems
to purge them of their grime. But all gas-jets are turned into
mere faint bilious blotches and outside the magic circle the
darkness, both on land and water, is intensified into ebon gloom.
And now for the daylight aspect of the yard, or rather yards.
An apology for untidiness on a contractor’s premises has a somewhat
droll sound, but one is made for the “muddle” in which the
“slop-yard” is found. The slop is just thawing after long
frost. A wide mass of dark, very unappetising batter-pudding
is pent up on the wharf, waiting for a barge to come alongside; when
a trap will be opened and the unsavoury mess cascade in a mudfall.
This accumulation of scavenging is indiscriminately called slop, but
formerly street dirt dirt used to be divided into mud and “mac,” the
latter being the product of traffic friction on macadamised roads,
and the more valuable for builders purposes because freer from
manure than mud. When I asked my obliging guide at what rate
the yard sold its slop, I was astonished to hear, “We get nothing,
give it away to brick-makers fifteen or sixteen miles down the
canal. Yes, the cost of the carriage falls on us too. We
own twenty barges, with two men and a horse apiece, and we hire as
well. The brick-makers know that we must get rid of the slop,
and so they won’t give us anything for it. If” he added, “the
yard were close to a country district, so that farmers could come
with their carts, they would be glad enough to pay us for it, it
makes excellent manure.”
Separate from the slop wharf by the gravel wharf, which, from its
contrast to its neighbours on both sides looks strangely clean and
almost goldenly bright, is the dust-yard. Outside the gates
empty dust and mud carts, so thickly furred with mud and dust that
the owners’ names are often almost illegible, are congregated in the
manner I have described. Other carts are rolling out empty and
rolling in full. One of them unfortunately goes over a poor
follow, who is taken up tenderly by two brother dusties and lifted
with care into a cab, backed into the yard to receive him, and in
this he is carried off to hospital in charge of a clerk.
The firm owns a hundred and twenty horses, manifestly well fed, and
they are well housed also. In their stables under the granary
which contains their hay, straw, chaff, and crushed oats, hot as
well as cold water is laid on for use at night. Their drivers
look as if they would be all the better for similar accommodation.
The dust that thickly covers the tracks in the yard is much like
that one flounders through in iron-works. Here the foot sinks
over the ankle in dry, black powder, and there sticks fast in
viscous, blacking-like mud. Even on a winter afternoon, with
the mercury dropping to freezing point, the perfumes floating, or,
rather brooding in the atmosphere are not those of Araby the Blest.
On a sweltering summer day, after a shower, what must be the odours
steaming up from such a conglomeration of ashes, egg-shells,
oyster-shells, herring-heads, greasy rags and bones, old boots and
shoes, and miscellaneous rubbish! And yet the people employed
in the yard, both men and women — so far as their flesh can be made
out through the dirt with which they have peppered and besmeared it
— look healthy, some quite plump and ruddy; and the same may be said
of the men who go out with the dust carts and the scavengers.
――――♦――――
APPENDIX IV.
BARGES USED BY JAMES DAVIES (TIMBER) MERCHANTS
LTD.
Colin Davies kindly provided the following information about barges
used by his family's firm of timber importers:
Names of some canal barges on Grand
Union Canal during 1950s and 1960s.
These barges could fit into the 14 locks between Brentford and Hayes
or West Drayton. Each could carry about 20 standards of timber
weighing about 50 tons.
The two principal lighterage companies were General Lighterage
Limited, which was known as “General”, and
The Thames Steam Tug and Lighterage Limited, which was
known as “Limited”. General usually took
the timber from The Surrey Docks via Brentford to Hayes, and
Limited usually took it to West Drayton.
|
GENERAL’S
BARGES |
|
Bullford
Cowford
Mayford
Westford
Uxford
Boxford
Norford |
Southford
Southall
Snar
Scaddle
Irvine
Isla
Gunner |
Trooper
Breech
Bore
Jemadar
Rissaldar
Sirdar
Pathan |
|
LIMITED’S
BARGES |
|
Hayesoak
Hayesbirch
Hayeswood
Hayesboard
Hayesroot
Hayes-etc. |
A few barges were a bit too wide to fit in the
locks via Brentford, and had to come the longer way round via
Regents Park. Some of these were called: Pam, Ripon,
Trunkfish, Brentbird, Brentwren.
I made a list like this while I was working with the forwarding
company in London (W. Hall) who organised the barges to come from
The Surry Docks to our wharves. We were having problem getting
enough canal barges to cope with our imports of timber, and I tried
to remember all the names of the barges that had ever come our way.
That way, I could make a guess at how many barges that were small
enough to get through the locks actually existed .
“General’s” barges had either names ending in Ford,
or names of places like Southall, or military names like
Gunner, Bore, Jemadar, or odd names like Isla,
Irvine, Scaddle, Snar.
“Limited’s” barges with names like Hayesroot, Hayeswood,
Hayesbirch were, according to my father, originally given
those names because they were specially built in the 1930s to carry
timber to the new JDT yard at Hayes. However, by the time I got to
work at Hayes in 1954, they were almost always carrying timber to
Yewsley/West Drayton for our other Co. called Davies Brothers (West
Drayton ) Ltd. That yard was alongside the canal by West Drayton
station. It was between the canal and the railway, and could take
cargoes delivered by rail as well as canal.
――――♦――――
APPENDIX V.
CONTROLLING CANAL CRAFT
(Grand Union Canal Company c. 1938)
Tell-tale Chart Shows Movement of Boats.
CHARTS of one
kind or another are to-day used in many industries as well as in
Government and Police Departments. While it might not be true to say
that the growth of the use of charts and maps owes its origin to the
planning on an intensive scale that took place during the War, it is
certain that since that world disturbance the use of charts and
plans has increased to an enormous extent. Scotland Yard, for
example, uses flags and maps to indicate districts in which crime
and road accidents are more serious than in others, and the Ministry
of Transport makes extensive use of maps and charts in its campaign
to reduce casualties on the roads. The London Passenger Transport
Board controls a vast organisation in which for many years the
control of traffic has been exercised by means of mechanism which
may not inaptly be called vitalised charts.
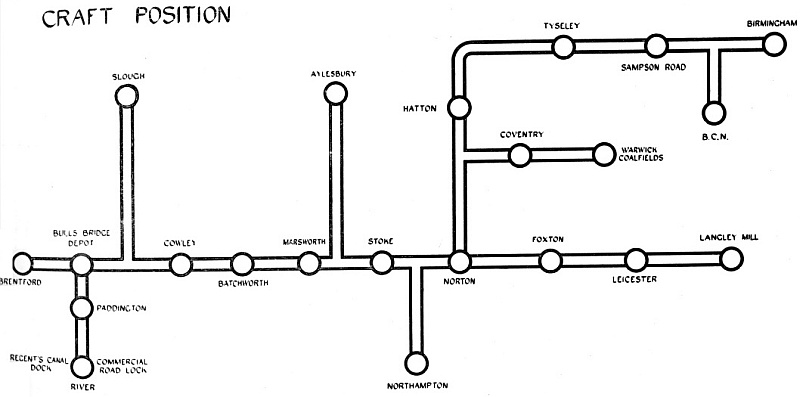
The Bulls Bridge control board,
Grand Union Canal Carrying Company.
Checking Movements of Craft.
In the early days of the Grand Union Canal Carrying Company Limited
it became apparent that some method whereby the movements of boats
could be checked and controlled was absolutely essential and the
necessity resulted in the adaptation of the chart idea to canal
craft.
Imagine then a line of boats five miles long and that will give some
idea of the size of the fleet of canal craft now controlled from the
Company’s Head Office in London. This fleet, which at the time of
writing consists of 380 boats, operates over three hundred miles of
waterway between such points as London, Northampton, Warwick,
Birmingham, Leicester, Nottingham, Loughborough, Rugby, Coventry,
and the coal producing areas of Warwickshire, Leicestershire, and
Nottinghamshire.
It will be realised that to control craft passing over such a large
area is no small task, but the difficulties involved have been
overcome so that the Company’s Traffic Department is now able to
ascertain almost at any moment the position of any unit of the
fleet.
Eliminating Empty Running.
Behind the scheme there is also the important consideration that the
aim should be to obtain the “best possible use” from
all craft and empty running eliminated as far as possible. The whole
scheme of control is carried out by the Staff as part of the normal
working of the Traffic Department, being entrusted to one officer.
The actual apparatus by which control is exercised is relatively
simple. A map about 11 ft. long and 4 ft. deep is stretched on one
of the walls of the office, and on it various important points on
the canal are shown in much the same way as stations appear on the
familiar maps so frequently issued in connection with the
underground railways of London. The map covers the whole area over
which the Company’s boats travel, and on it appear twenty-four
coloured circles representing Reporting Offices, from each of which
every morning the Head Office receives a report. Thus, at 9 o’clock
each morning in the Company’s Traffic Department the clerk in charge
of boat control, having obtained all the reports, spreads them out
in front of him on the long desk underneath the map. On his left
hand on the wall is the London area, with its reporting points at
Regent’s Canal Dock, Paddington, Bull’s Bridge, Brentford, and
Cowley. On his right hand are the Birmingham, Leicester and Coventry
areas, while in front of him are the intermediate points and the
rack containing numbered ivorine discs which represent boats, red
for loaded boats and green for empty boats.
The reports from the various terminals and observation points are
sorted and then begins the task of moving the “boats”. The terminal
reports show which boats are discharging and loading and alternately
those awaiting orders. The requisite discs are selected from the
rack or from the position previously reported and transferred to the
appropriate point. Boats in transit are moved from one position to
another in accordance with the information shown on the reports and
are always kept on the right-hand side of the route.
In addition to providing a quick means of reference to the position
of all craft, the map also enables slow moving boats to be traced as
the points are so selected that a boat should pass at least one
office during the day, and its failure to do so is at once apparent,
for when the rest of the boats are moved from the previous point the
laggard will still remain.
Not the least useful function served by the chart is that it
indicates the number of boats which will be arriving at any one
point and thus requirements at loading points can be met by moving
empty craft accordingly.
――――♦――――
[Chapter
XI.] |